- Writer: Dell SecureWorks Counter Menace Unit™ Menace Intelligence
- Date: 27 August 2014
Overview
In late February 2014, the Dell SecureWorks Counter Menace Unit™ (CTU™) research staff analyzed a household of file-encrypting ransomware being actively distributed on the Web. Though this ransomware, now often known as CryptoWall, turned well-known within the first quarter of 2014, it has been distributed since at the very least early November 2013. CTU researchers contemplate CryptoWall to be the biggest and most harmful ransomware menace on the Web as of this publication, they usually count on this menace to proceed rising.
Background
After the emergence of the notorious CryptoLocker ransomware in September 2013, CTU researchers noticed an rising variety of ransomware households that destroyed information along with demanding cost from victims. Whereas comparable threats have existed for years, this tactic didn’t turn out to be widespread till CryptoLocker’s appreciable success. Historically, ransomware disabled victims’ entry to their computer systems by means of non-destructive means till the victims paid for the computer systems’ launch.
Early CryptoWall variants intently mimicked each the habits and look of the real CryptoLocker (see Determine 1). The precise an infection vector of those early infections isn’t often known as of this publication, however anecdotal stories from victims counsel the malware arrived as an electronic mail attachment or drive-by obtain. Proof collected by CTU researchers within the first a number of days of the February 2014 marketing campaign confirmed at the very least a number of thousand world infections.
Determine 1. Early CryptoWall variants (left) mimicked CryptoLocker (proper). (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
As illustrated by a pattern uploaded to the VirusTotal analysis service, CryptoWall has had a number of names. CTU researchers known as early variants “CryptoClone” as a consequence of an absence of a novel identify provided by the menace actors. In mid-March 2014, the authors revealed that the true identify of this malware was CryptoDefense. In early Might 2014, the malware’s identify was once more modified to CryptoWall.
Whereas neither the malware nor infrastructure of CryptoWall is as refined as that of CryptoLocker, the menace actors have demonstrated each longevity and proficiency in distribution. Similarities between CryptoWall samples and the Tobfy household of conventional ransomware counsel that the identical menace actors could also be liable for each households, or that the menace actors behind each households are associated.
An infection
CryptoWall has unfold by means of varied an infection vectors since its inception, together with browser exploit kits, drive-by downloads, and malicious electronic mail attachments. Since late March 2014, it has been primarily distributed by means of malicious attachments and obtain hyperlinks despatched by means of the Cutwail spam botnet. These Cutwail spam electronic mail attachments sometimes distribute the Upatre downloader, which retrieves CryptoWall samples hosted on compromised web sites. Upatre was the first methodology of distributing the Gameover Zeus banking trojan till Operation Tovar disrupted that ecosystem in Might 2014. Upatre has additionally been used to distribute the Dyre banking trojan. In June 2014, the malicious emails started together with hyperlinks to respectable cloud internet hosting suppliers resembling Dropbox, Cubby, and MediaFire. The hyperlinks level to ZIP archives that include a CryptoWall executable.
On June 5, 2014, an aggressive spam marketing campaign launched by Cutwail led to the biggest single-day an infection charges noticed by CTU researchers as of this publication. These emails used a typical “missed fax” lure that included hyperlinks to Dropbox. This spam marketing campaign paused over the weekend however resumed in earnest on June 9-10 with emails purporting to be from monetary establishments or authorities businesses, as proven in Determine 2.
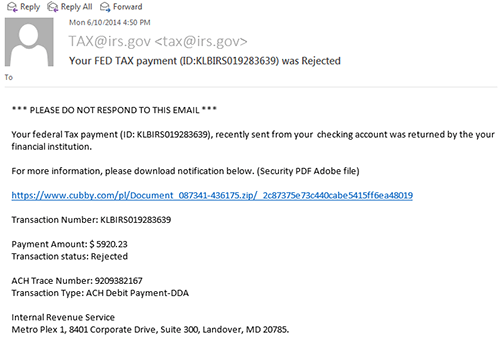
Determine 2. Faux tax cost rejection discover despatched by Cutwail on June 10, 2014. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
On each Might 25 and Might 28, simply previous to this spam marketing campaign, safety researchers noticed the Angler exploit equipment distributing CryptoWall. The RIG exploit equipment was additionally noticed distributing this malware between Might 19 and Might 30. In early Might, the Infinity exploit equipment (also referred to as Goon and Redkit V2) was infecting techniques with CryptoWall.
Since CryptoWall’s emergence in late February 2014, CTU researchers have noticed regular however low-level an infection charges on Dell SecureWorks shopper networks. The menace actors behind CryptoWall elevated the quantity of its distribution in mid-Might, leading to a marked development in infections (see Determine 3).
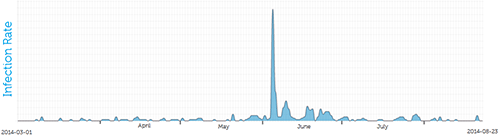
Determine 3. CryptoWall infections noticed on Dell SecureWorks shopper networks. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
On February 26, 2014, CTU researchers registered a site utilized by the CryptoWall malware as a backup command and management (C2) server. By means of June 13, this sinkhole acquired connections from 968 distinctive hosts that seemed to be contaminated with early CryptoWall variants (see Determine 4).
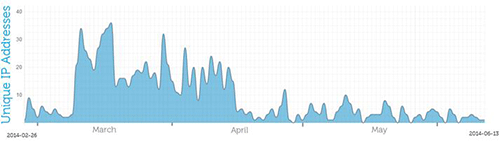
Determine 4. Distinctive IP addresses contacting a sinkhole from February 26 to June 13, 2014. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
The geographic distribution of contaminated techniques indicated a bias in direction of techniques in Asian and Center Jap international locations, as proven in Desk 1.
| Nation | Contaminated techniques | Share of whole |
| India | 266 | 27.5% |
| United States | 141 | 14.6% |
| Iran | 112 | 11.6% |
| Singapore | 93 | 9.6% |
| Poland | 55 | 5.7% |
| Pakistan | 49 | 5.1% |
| Turkey | 42 | 4.3% |
| Brazil | 40 | 4.1% |
| Sri Lanka | 27 | 2.8% |
| Indonesia | 23 | 2.4% |
Desk 1. Geographic breakdown of an infection counts.
Each new an infection is assigned a novel alphanumeric code (Base 36), which is allotted sequentially by the CryptoWall backend (e.g., aaaa, aaab, aaac). Between mid-March and August 24, 2014, practically 625,000 techniques have been contaminated with CryptoWall. In that very same timeframe, CryptoWall encrypted greater than 5.25 billion recordsdata. CTU researchers queried the ransom cost server utilizing the codes assigned to every of those techniques and picked up the IP handle, approximate time of an infection, and cost standing for every an infection.
Determine 5 reveals the geographic distribution of those compromised techniques. Each nation on the planet had at the very least one sufferer. Many of the infections are in the USA as a consequence of CryptoWall’s frequent distribution by means of Cutwail spam focusing on English-speaking customers.
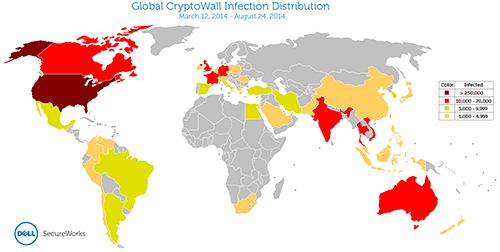
Determine 5. World distribution of CryptoWall infections between March 12 (approximate) and August 24, 2014. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
Desk 2 lists the highest ten affected international locations.
| Nation | Contaminated techniques | Share of whole |
| United States | 253,521 | 40.6% |
| Vietnam | 66,590 | 10.7% |
| United Kingdom | 40,258 | 6.4% |
| Canada | 32,579 | 5.2% |
| India | 22,582 | 3.6% |
| Australia | 19,562 | 3.1% |
| Thailand | 13,718 | 2.2% |
| France | 13,005 | 2.1% |
| Germany | 12,826 | 2.1% |
| Turkey | 9,488 | 1.5% |
Desk 2. Geographic breakdown of an infection counts.
Every CryptoWall pattern is marked with a “marketing campaign ID” that is transmitted to the C2 server during communication. The threat actors use this ID to track samples by infection vector. For example, the “cw400” marketing campaign was used for samples distributed by Cutwail (both by means of Upatre, direct attachment, or externally linked). Desk 3 lists the campaigns recognized by CTU researchers. The date ranges are based mostly on the very best accessible proof. These marketing campaign identifiers is also used to implement an associates program. Nevertheless, as of this publication, CryptoWall is considered managed and utilized by a single menace group.
| Marketing campaign ID | Interval | An infection vector |
| analteen | November 5-11, 2013 | Drive-by obtain |
| orgasm | November 8, 2013 | Unknown |
| obamagay1 | December 30, 2013 – January 1, 2014 | Unknown |
| wolfgang | February 9-26, 2014 | Unknown |
| porno2 | February 26, 2014 | Unknown |
| crypt1 | February 26, 2014 | Unknown |
| crypt11 | March 8-10, 2014 | Unknown |
| def001 | March 17 – April 17, 2014 | Cutwail/Upatre |
| def002 | March 21, 2014 | Unknown |
| def003 | April 2-7, 2014 | Cutwail/Upatre |
| def004 | April 4-25, 2014 | Unknown |
| def006 | April 10, 2014 | Unknown |
| def007 | April 12-17, 2014 | Unknown |
| def201 | April 28, 2014 | Unknown |
| def009 | April 29 – Might 9, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw800 | Might 3-20, 2014 | Infinity/Goon exploit equipment |
| cw100 | Might 9, 2014 – In use as of this publication | Magnitude exploit equipment |
| cw1500 | Might 14 – June 5, 2014 | Angler exploit equipment |
| cw200 | Might 21, 2014 | RIG exploit equipment |
| cw400 | Might 21, 2014 – In use as of this publication | Cutwail |
| cw900 | Might 21-23, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw700 | Might 29-30, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw1600 | June 3-20, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw1900 | Might 26 – June 6, 2014 | Nuclear exploit equipment/Pony Loader |
| cw2200 | June 10 – July 4, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw2300 | June 11, 2014 | Unknown |
| cw2400 | Unknown | Unknown |
| cw2500 | June 19, 2014 – In use as of this publication | Gozi/Neverquest |
| cw404 | June 26, 2014 – In use as of this publication | Cutwail |
| cw2700 | July 8-15, 2014 | Unknown |
| tor003 | July 21, 2014 | Unknown |
| tor2800 | July 25, 2014 | Cutwail |
| cw2800 | August 4, 2014 – In use as of this publication | Unknown |
Desk 3. CryptoWall marketing campaign identifiers, time ranges, and an infection vectors.
Execution and persistence
When CryptoWall is first executed, it unpacks itself in reminiscence and injects malicious code into new processes that it creates. It creates an “explorer.exe” course of utilizing the respectable system binary in a suspended state and maps and executes malicious code into the method’s handle area. This malicious occasion of explorer.exe then executes the next course of:
- vssadmin.exe Delete Shadows /All /Quiet
This course of causes the Home windows Quantity Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to delete all shadow copies of the file system. CryptoWall additionally disables Home windows’ System Restore characteristic by modifying the registry key:
- HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionSystemRestore => DisableSR
Each methods stop contaminated techniques from recovering encrypted recordsdata.
Lastly, the malicious code creates a “svchost.exe -k netsvcs” course of, once more utilizing the respectable system binary. The malicious svchost.exe course of is anomalous, because it runs with the privileges of the sufferer system’s consumer and never as a system course of (see Determine 6). Moreover, the method runs independently and doesn’t seem as a baby means of companies.exe.
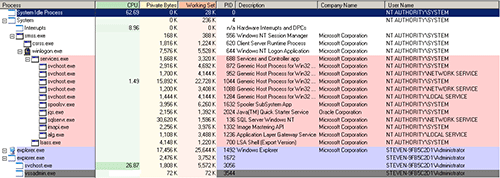
Determine 6. CryptoWall masquerading as a respectable system course of. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
To determine persistence throughout system reboots, a replica of the malware is positioned in %AppData%, %UserProfilepercentBegin MenuProgramsStartup, and a listing on the root of the system drive. Then the malware provides a number of “autostart” registry keys (see Figure 7). Some CryptoWall variants also install a “RunOnce” key prefixed with an asterisk, which causes the executable to run even in Secure Mode. Every pattern is configured to make use of a sure six hexadecimal character filename (e.g., 3e0d6a) that the malware makes use of in different variations (e.g., 3e0d6a9).
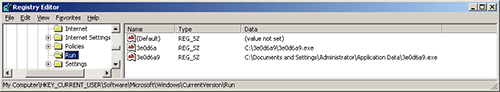
Determine 7. Registry keys added to ascertain persistence. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
More moderen CryptoWall variants terminate after efficiently encrypting recordsdata and notifying the C2 server. On the time of analysis, the malware will not be executing in reminiscence on techniques affected by these variants, however the persistence mechanisms stay and be sure that the malware runs upon system reboot.
Community communication
CryptoWall makes use of an unremarkable C2 system that depends on a number of static domains hard-coded into every binary. In contrast to different prevalent malware households, CryptoWall doesn’t use superior methods resembling area era algorithms (DGA) or fast-flux DNS techniques. Though CryptoWall makes use of the WinINet software programming interface (API) to carry out community features, the malware ignores the system’s configured proxy server and as a substitute communicates instantly with its C2 servers.
As soon as CryptoWall is lively on a compromised system, it sends an preliminary phone-home message to the C2 server over HTTP on TCP port 80 (see Determine 8).
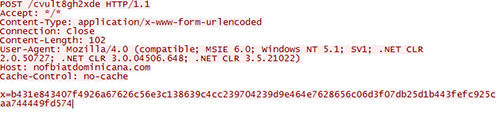
Determine 8. CryptoWall phone-home community site visitors. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
These servers use the Privoxy non-caching internet proxy and sure act as first-tier servers that proxy site visitors from victims to backend servers that handle encryption keys. In late July 2014, a number of distributed samples used C2 servers hosted on the Tor community, which can point out the operators intend to finally cease utilizing conventional, instantly accessible servers.
The requested object is the RC4 key used to encrypt the knowledge contained within the POST parameter. The unencrypted request has the next format:
- 4
The “cw1900” string represents the CryptoWall binary’s marketing campaign. The string of 32 hexadecimal characters is a novel an infection identifier derived from the compromised system’s laptop identify, disk quantity serial quantity, processor data, and OS model (see Determine 9). This string can be used as a mutex that stops a number of copies from infecting the identical system.
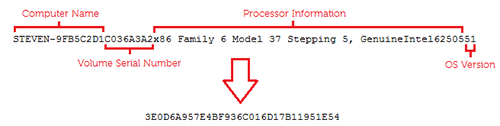
Determine 9. Distinctive an infection identification string era. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
An lively C2 server responds with information encrypted with the identical RC4 key. Every request initiated by the compromised system makes use of a brand new RC4 key. After a compromised system efficiently contacts an lively C2 server, the system sends a second request that prompts the C2 server to ship the next reply (proven unencrypted):
kpai7ycr7jxqkilp.onion
This reply consists of the Tor cost web site, distinctive cost identifier, nation code of the compromised system, and the general public key part of the RSA-2048 key pair to encrypt system recordsdata. The distinctive cost identifier permits the sufferer to navigate to the decryption web page particular to their an infection. This identifier differs from the distinctive an infection identifier proven in Determine 9, which the menace actors use to determine victims and affiliate them with the saved RSA non-public key.
The malware often beacons to the C2 server through the encryption course of. As soon as encryption is full, the malware notifies the C2 server what number of recordsdata have been encrypted:
- 3
The malware doesn't exfiltrate consumer credentials, recordsdata, or metadata about recordsdata. Early CryptoWall variants did transmit a screenshot of the contaminated system again to the C2 server, however this performance has not been current in variants distributed since mid-March 2014.
File encryption
File encryption begins after CryptoWall efficiently retrieves the RSA public key from an lively C2 server. Subsequently, utilizing network-based controls to dam this communication can stop compromised techniques from turning into encrypted. In contrast to CryptoLocker's use of a symmetric cipher, resembling AES, to encrypt bulk information, CryptoWall makes use of the RSA public key to instantly encrypt recordsdata. As a result of the RSA algorithm is way extra computationally intensive than symmetric ciphers, compromised techniques expertise vital CPU load after CryptoWall compromises as recordsdata are encrypted.
The primary express indication of an lively an infection offered to a sufferer is the net web page that CryptoWall opens after encrypting the recordsdata (see Determine 10).
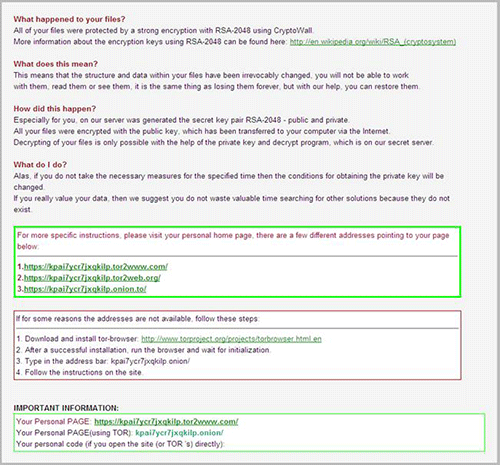
Determine 10. CryptoWall "splash" display screen offered to victims. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
CryptoWall variants deployed earlier than April 1, 2014 contained a weak point within the cryptographic implementation that allowed restoration of the important thing used to encrypt recordsdata. This flaw seems to have been corrected in later variations of the malware. CTU researchers haven't carried out a rigorous evaluation of CryptoWall's cryptographic implementation, however they haven't found any apparent flaws that permit decryption with out cost.
CryptoWall recursively navigates the file system, selectively encrypting sure file varieties (e.g., textual content recordsdata, paperwork, supply code). Executables and DLLs are left unmodified to forestall the compromised system from turning into corrupted and unusable. Desk 4 lists the focused file extensions.
| *.c | *.h | *.m | *.ai | *.cs | *.db | *.db | *.nd |
| *.pl | *.ps | *.py | *.rm | *.3dm | *.3ds | *3fr | *.3g2 |
| *.3gp | *.ach | *.arw | *.asf | *.asx | *.avi | *.bak | *.bay |
| *.cdr | *.cer | *.cpp | *.cr2 | *.crt | *.crw | *.dbf | *.dcr |
| *.dds | *.der | *.des | *.dng | *.doc | *.dtd | *.dwg | *.dxf |
| *.dxg | *.eml | *.eps | *.erf | *.fla | *.flv | *.hpp | *.iif |
| *.jpe | *.jpg | *.kdc | *.key | *.lua | *.m4v | *.max | *.mdb |
| *.mdf | *.mef | *.mov | *.mp3 | *.mp4 | *.mpg | *.mrw | *.msg |
| *.nef | *.nk2 | *.nrw | *.oab | *.obj | *.odb | *.odc | *.odm |
| *.odp | *.ods | *.odt | *.orf | *.ost | *.p12 | *.p7b | *.p7c |
| *.pab | *.pas | *.pct | *.pdb | *.pdd | *.pef | *.pem | |
| *.pfx | *.pps | *.ppt | *.prf | *.psd | *.pst | *.ptx | *.qba |
| *.qbb | *.qbm | *.qbr | *.qbw | *.qbx | *.qby | *.r3d | *.raf |
| *.uncooked | *.rtf | *.rw2 | *.rwl | *.sql | *.sr2 | *.srf | *.srt |
| *.srw | *.svg | *.swf | *.tex | *.tga | *.thm | *.tlg | *.txt |
| *.vob | *.wav | *.wb2 | *.wmv | *.wpd | *.wps | *.x3f | *.xlk |
| *.xlr | *.xls | *.yuv | *.again | *.docm | *.docx | *.flac | *.indd |
| *.java | *.jpeg | *.pptm | *.pptx | *.xlsb | *.xlsm | *.xlsx |
Desk 4. File extensions focused for encryption.
Information on fastened (e.g., laborious disks), detachable (e.g., USB reminiscence), and community drives (when mapped to a drive letter) are focused for encryption. Moreover, cloud storage companies, resembling Dropbox or Google Drive, which are mapped to a focused file system may also be encrypted. Sometimes, encrypted recordsdata are 5 to 10 p.c bigger than their authentic variations. CryptoWall marks encrypted recordsdata by prepending a customized header (see Determine 11).
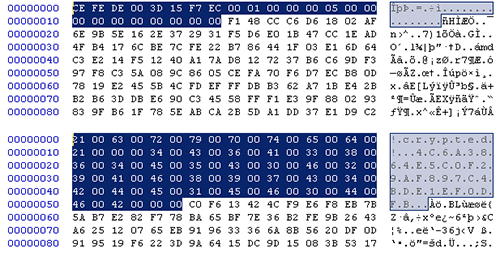
Determine 11. Encrypted recordsdata from early (backside) and later (prime) CryptoWall variants. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
CryptoWall leaves three "DECRYPT_INSTRUCTIONS" recordsdata with .url, .txt, and .html extensions in every listing it traverses. These recordsdata include details about the an infection and directions on how to pay the ransom.
The CTU research staff discourages victims from paying ransoms as a result of it facilitates the expansion of cybercrime enterprises. Victims who select to pay the ransom submit cost and wait an arbitrary period of time for the menace actors to substantiate the cost. As soon as the cost has been confirmed, the sufferer's web page on the cost server displays the adjustments proven in Determine 12.
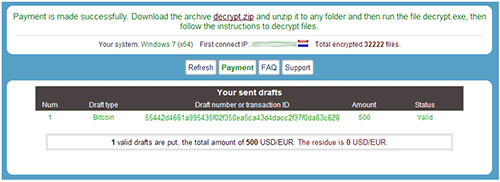
Determine 12. Redacted sufferer touchdown web page after cost affirmation. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
A "decrypt.zip" archive contains a small (30 KB) decryption program ("decrypt.exe") and the victim's secret RSA key ("secret.key") in Microsoft Cryptographic Supplier key BLOB format. The decryption program is a UPX-packed executable that's uniquely generated for every sufferer after cost.
Fee
Like CryptoLocker, earlier CryptoWall variants included quite a few cost choices, together with pre-paid playing cards resembling MoneyPak, Paysafecard, cashU, and Ukash along with the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. In contrast to CryptoLocker, the CryptoWall menace actors initially accepted Litecoin (see Determine 13); nonetheless, the one noticed Litecoin handle (LTv4m4y7NKHCXdw31dSEpTJmP6kXTinWDy) by no means acquired any funds.
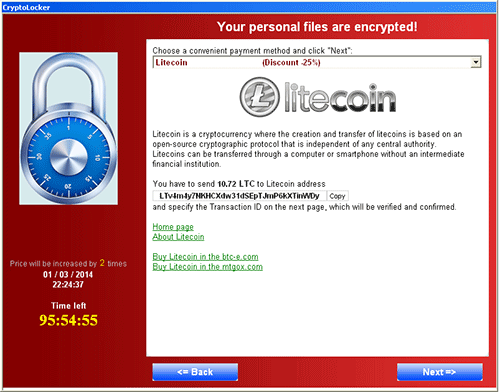
Determine 13. Litecoin cost choice in early CryptoWall variants. (Supply: Dell SecureWorks)
The ransom has steadily fluctuated on the whim of the botnet operators, and no actual sample has been established that determines which victims obtain a specific ransom worth. Ransoms starting from $200 to $2,000 have been demanded at varied instances by CryptoWall's operators. The bigger ransoms are sometimes reserved for victims who don't pay inside the allotted time (normally 4 to 7 days). In a single case, a sufferer paid $10,000 for the discharge of their recordsdata.
The online web page that instructs victims how to pay the ransom shows a static Bitcoin handle that's rotated at the very least as soon as per day. Desk 5 lists recognized Bitcoin addresses, the variety of ransoms collected, the worth in bitcoins of these acquired ransoms, and the worth in U.S. {dollars} as of August 24, 2014. CTU researchers instantly noticed all of the addresses in Desk 5 in use on the CryptoWall cost servers, besides those indicated in daring. The addresses in daring have been found retrospectively by analyzing the transaction historical past of the Bitcoin community for addresses possible receiving ransom funds.
| Tackle | Collected (BTC) | Collected (USD) |
| 1EmLLj8peW292zR2VvumYPPa9wLcK4CPK1 | 62.2634 | $32,377 |
| 16N3jvnF7UhRh74TMmtwxpLX6zPQKPbEbh | 21.2352 | $11.042 |
| 19yqWit95eFGmUTYDLr3memcDoJiYgUppc | 56.4450 | $29,351 |
| 1ApF4XayPo7Mtpe326o3xMnSgrkZo7TCWD | 71.9387 | $37,408 |
| 19DyWHtgLgDKgEeoKjfpCJJ9WU8SQ3gr27 | 29.4246 | $15,301 |
| 1LGnuv6KX9SXB8eM72dnBAcECeaC8Z2zje | 1.6000 | $832 |
| 1K81FeS3TH7DkqrMECtVDwXruRiXPXa6dZ | 14.9798 | $7,790 |
| 1PnPJfx4ct8YHRnTnx1VrSnrZeQik86BXa | 40.0517 | $20,827 |
| 14bD9RgtJeKxdJMm5SRbmzFcsk8azTheR9 | 9.4715 | $4,925 |
| 1GkBo7k4b1k7ehPYYqiY9jhGXPNCKtyEGi | 6.0605 | $3,151 |
| 1L7SLmazbbcy614zsDSLwz4bxz1nnJvDeV | 48.9531 | $25,456 |
| 1HYDwtwtotSedCDCHDcgbRks2a7yPcicwd | 67.4567 | $35,077 |
| 1CgD9eHj75MP1thzhqU1nEb5jyjkYfMMbK | 17.9618 | $9.340 |
| 1CeA899xpo3Fe6DQwZwEkd6vQfRHoLuCJD | 82.0797 | $42,681 |
| 1M4pN4rH4LfXuTaJCL5tpnXJkbVRC35saU | 9.6855 | $5,036 |
| 1FUEYosFFP9X93yrPzeW5YQpbtpg8eq5Gd | 2.4603 | $1,279 |
| 18e6Wtkvpf4L9RHwzbgvR9QTUVm1yBybwu | 15.9021 | $8,269 |
| 17JmFhoJhFKinrKm6XK3LgSmuzfzWyE6gi | 8.8915 | $4,624 |
| 1MrnUHFADbj5S9ERJ9bGXtQvhx81TFztMN | 17.2850 | $8,988 |
| 1LPAUi1LWzCsRLkGFWFdN5sENs1LufBfNp | 33.4070 | $17,372 |
| 1JTEjiizLihT6GbvoW52Abmg6rV1KyD3fw | 40.8381 | $21,236 |
| 1ASm3RVYjjpLmMTECCkoy8yLmUN9rmE9aS | 12.8446 | $6,679 |
| 1Pa7ZkA9JHzwp8FazU4YBVSiYFPP3majgA | 18.5848 | $9,664 |
| 1FAB6uvKD9q5MnGm3ta1ERvmeVpYgyNQwj | 20.0374 | $10,419 |
| 1M8oK3D2G8ipTy7sCxiatrHC35CpAgmrrw | 76.7055 | $39,887 |
| 1DDPoA3rnXtHtp71v3KAtd53pdRTmskxrK | 9.3686 | $4,872 |
| 16yd1Wj2NZa2uLZ6W4UDCDJ2Ttw92uFaT7 | 28.1476 | $14,637 |
| 1BhLzCZGY6dwQYgX4B6NR5sjDebBPNapvv | 2.7601 | $1,435 |
| 1LV8hdp4rTfRESUT3FoZhgxnSW4xthqpS3 | 2.1511 | $1,119 |
| 1AkJptnuoiQAD3GmHMFHBSMxZ9H2GKJTkB | 32.4437 | $16,871 |
| 14ytdF3C9VRbttMfh9J56yR9ZWqfmFbBWN | 11.2697 | $5,860 |
| 13BeAzA4mhwDYJEwhqNd2LsUnuhuVqKvw8 | 17.0646 | $8,874 |
| 1PgsYJKnnKk1mxLGY9hHFgtuBffGx2E9HR | 10.0326 | $5,217 |
| 13Kqgurx7eQg3G29NwV7ouJ8UHJRSUwwAe | 39.5325 | $20,557 |
Desk 5. Recognized CryptoWall Bitcoin addresses and acquired switch totals.
The overall influx to the addresses in Desk 5 is roughly 939 BTC. On the BTC trade charge as of August 24, 2014 (1 BTC = $520), menace actors have acquired greater than $488,000 in ransoms. These funds symbolize a subset of the overall CryptoWall funds considered acquired. Some funds made to those addresses didn't match the sample of CryptoWall ransom funds and could also be revenue from different, unrelated felony exercise.
Information collected instantly from the ransom cost server reveals the precise variety of paying victims in addition to the quantity they paid. Of practically 625,000 infections, 1,683 victims (0.27%) paid the ransom, for a complete take of $1,101,900 over the course of six months. The distribution of ransom funds is proven in Desk 6.
| Ransom quantity | Quantity paid | Share |
| $200 | 6 | 0.4% |
| $500 | 1,087 | 64.6% |
| $600 | 3 | 0.2% |
| $750 | 122 | 7.2% |
| $1000 | 399 | 23.7% |
| $1500 | 27 | 1.6% |
| $1750 | 1 | |
| $2000 | 6 | 0.4% |
| $10000 | 1 |
Desk 6. Distribution of ransom funds made by victims.
Primarily based on autopsy information collected by researchers, CryptoWall has been much less efficient at producing revenue than CryptoLocker. Each malware households accepted funds through Bitcoin, with 0.27% of CryptoWall victims and 0.21% of CryptoLocker victims paying ransoms in bitcoins. CryptoLocker additionally accepted MoneyPak, and an extra 1.1% of victims paid ransoms utilizing pre-paid MoneyPak playing cards. As of this publication, CryptoWall has solely collected 37% of the overall ransoms collected by CryptoLocker regardless of infecting practically 100,000 extra victims. CryptoWall's larger common ransom quantities and the technical boundaries typical customers encounter when making an attempt to acquire bitcoins has possible contributed to this malware household's extra modest success. Moreover, it's possible the CryptoWall operators don't have a classy "cash out" and laundering operation just like the Gameover Zeus crew and can't course of pre-paid playing cards in such excessive volumes.
Conclusion
In mid-March 2014, CryptoWall emerged because the main file-encrypting ransomware menace. The menace actors behind this malware have a number of years of profitable cybercrime expertise and have demonstrated a variety of distribution strategies. In consequence, CTU researchers count on this menace will proceed to develop.
The next actions could mitigate publicity to or injury from CryptoWall:
- Block executable recordsdata and compressed archives containing executable recordsdata earlier than they attain a consumer's inbox.
- Maintain working techniques, browsers, and browser plugins, resembling Java and Silverlight, absolutely up to date to forestall compromises ensuing from publicity to take advantage of kits.
- Aggressively block recognized indicators from speaking together with your community to quickly neuter the malware till it may be found and eliminated.
- Reevaluate permissions on shared community drives to forestall unprivileged customers from modifying recordsdata.
- Commonly again up information with so-called "cold" offline backup media. Backups to domestically linked, network-attached, or cloud-based storage should not adequate as a result of CryptoWall encrypts these recordsdata together with these discovered on the system drive.
Software program Restriction Insurance policies (SRPs) don't successfully mitigate CryptoWall as a result of method the malware infects techniques.
Menace indicators
To mitigate publicity to the CryptoWall malware, CTU researchers suggest that shoppers use accessible controls to limit entry utilizing the indications in Desk 7. The domains and IP addresses listed within the indicator desk could include malicious content material, so contemplate the dangers earlier than opening them in a browser.
| Indicator | Kind | Context |
| youtubeallin.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| serbiabboy.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| hairyhustler.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| yoyosasa.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| uprnsme.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| dealwithhell.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| wawamediana.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| qoweiuwea.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| dominikanabestplace.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| nofbiatdominicana.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| dominicanajoker.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| likeyoudominicana.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| khalisimilisi.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| posramosra.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| maskaradshowdominicana.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| newsbrontima.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| yaroshwelcome.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| granatebit.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| rearbeab.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| droterdrotit.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| kukisasda8121.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| tyuweirwsdf18741.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| machetesraka.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| markizasamvel.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| wachapikchaid91.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| hilaryclintonbest81.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| niggaattack23.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| norevengenosuck.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| stopobamastopusa.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| jiromepic.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| clocksoffers.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| gretableta.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| kaikialexus.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| babyslutsnil.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| wartbartmart.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| la4eversuck.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| obsesickshit.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| mamapapafam.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| usawithgitler.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| kickasssisters.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| bdsmwithyou.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| iampeterbaby.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| teromasla.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| torichipinis.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| gitlerluvua.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| covermontislol.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| usaalwayswar.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| bolizarsospos.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| titaniumpaladium.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| adolfforua.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| vivatsaultppc.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| milimalipali.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| poroshenkogitler.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| waltabaldasd.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| dancewithmeseniorita.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| indeedlinkme.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| crunkthatme.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| hungarymethis.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| terrymerry.com | Area identify | C2 server |
| lvoobptv6w5zanxu.onion | Tor handle | C2 server |
| hyzcrtwh6ispjwj4.onion | Tor handle | C2 server |
| 2yd2bu2k5ilgxv6u.onion | Tor handle | C2 server |
| kpai7ycr7jxqkilp.onion | Tor handle | Fee server |
| 78.110.175.80 | IP handle | C2 server (United Kingdom) |
| 192.64.115.86 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 5.101.146.182 | IP handle | C2 server (United Kingdom) |
| 199.188.203.16 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 46.19.143.234 | IP handle | C2 server (Switzerland) |
| 162.213.250.163 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 192.64.115.91 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 141.255.167.3 | IP handle | C2 server (Switzerland) |
| 199.188.206.202 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 185.12.44.5 | IP handle | C2 server (Switzerland) |
| 194.58.101.3 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 192.31.186.3 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 31.31.204.59 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 194.58.101.96 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 194.58.101.112 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 194.58.101.111 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 151.248.124.30 | IP handle | C2 server (Russia) |
| 199.127.225.232 | IP handle | C2 server (United States) |
| 3769639c17f0cd5045964b0839c9f009 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 03467f231a3fce6795545ae99a6dad161effa3bf681031693815eabf1648ee66 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 85f830c85cc881358dfb631ef1f54a1a | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 7ed58ef4fd3dc4efaea9e595614553445afb055c0c675b692f12a5629251b040 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| b6c7943c056ace5911b95d36ff06e0e4 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| d5a70ba5a194ab737fc52b9f4283ce9d32f090590aea34224f7ea9ec63557a4f | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| b30a8168ff49145d7d3cdcfd47dbfaef | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 23eae15fbd3fff11ae9c0a74dec2f078a0213b6df54cf0011a0f5feae20437ec | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 167f16c8ae349cfb7d450cdf335dd9ca | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| fa706ed93469c257ee1531ddcf57bbab8734f3d092712158faf4e27656ab832e | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| a7e38522f8ff161968f72d8bcc956b4e | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| fc5e57f70bdce3af0e8c43d124eacd1ead0be79bf369284f85a5f81c629f345e | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| f612500ee9764e18ca78d2e78df5b017 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 7351e53bd863795104d609f2192e3436d3a07fb597f0bab35d175df88a34c3e0 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| e36bbd682b5dd435baec8ec268c9c825 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| d14f1d1e07bd116ed0faf5896438177f36a05adacf5af4f32910e313e9c1fd93 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 44150a32a84d3e1e07a042c3042a854c | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 114df2c77884312fc58d48bb6c4eb2ae23bbea2c37aad29c6fc0f544d7a16e36 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 189d1d0c7ec162533b4aff4b8d0e95b1 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| a7c2b304848f18c412776e5f461b42186b690eeed7b2955522f9fe716cfa3876 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 3e9929a6751f184cb71d3c4adfc6fb78 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| ab89a375ba9a0ec6ddc875ddde7647c4d2a140b07233580b143e0ca9aaf581f5 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 2fde49072741d59fd941b494403b9b0f | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 63d4965ed89e6951bb68f5e76a28f7f9512bf3feb64fcedfc3b98bc72dbcd070 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 934b014689771a7689c70cd179c8bd71 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| a66b62735473fe257d35d003eb71aeb832e055d6f727e42ef1880c4d054118bb | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| fc8db5b43ddf09bf0f03171e262495f6 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| 47faaf4ab59c18ad9c72df1bec65873c350b5d72f361a723ae5f8b279a5b6b22 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
| 00b536d9838b3e19d0ded1a6612a8b53 | MD5 hash | Malware pattern |
| a3ccdcf57d11314b8db4733eb67ab06f41a710c2e3404a26e5390465bcff7609 | SHA256 hash | Malware pattern |
Desk 7. Indicators for CryptoWall ransomware.
