Over the previous couple of years, cryptocurrency hacking has develop into a pervasive and formidable menace, resulting in billions of {dollars} stolen from crypto platforms and exposing vulnerabilities throughout the ecosystem. As we revealed in final yr’s Crypto Crime Report, 2022 was the largest yr ever for crypto theft with $3.7 billion stolen. In 2023, nevertheless, funds stolen decreased by roughly 54.3% to $1.7 billion, although the variety of particular person hacking incidents really grew, from 219 in 2022 to 231 in 2023.
Why the massive drop in stolen funds? Principally as a consequence of a drop in DeFi hacking. Hacks of DeFi protocols largely drove the massive enhance in stolen crypto that we noticed in 2021 and 2022, with cybercriminals stealing greater than $3.1 billion in DeFi hacks in 2022. However in 2023, hackers stole simply $1.1 billion from DeFi protocols. This quantities to a 63.7% drop within the complete worth stolen from DeFi platforms year-over-year. There was additionally a big drop within the share of all funds stolen accounted for by DeFi protocol victims in 2023, as we see on the chart beneath.
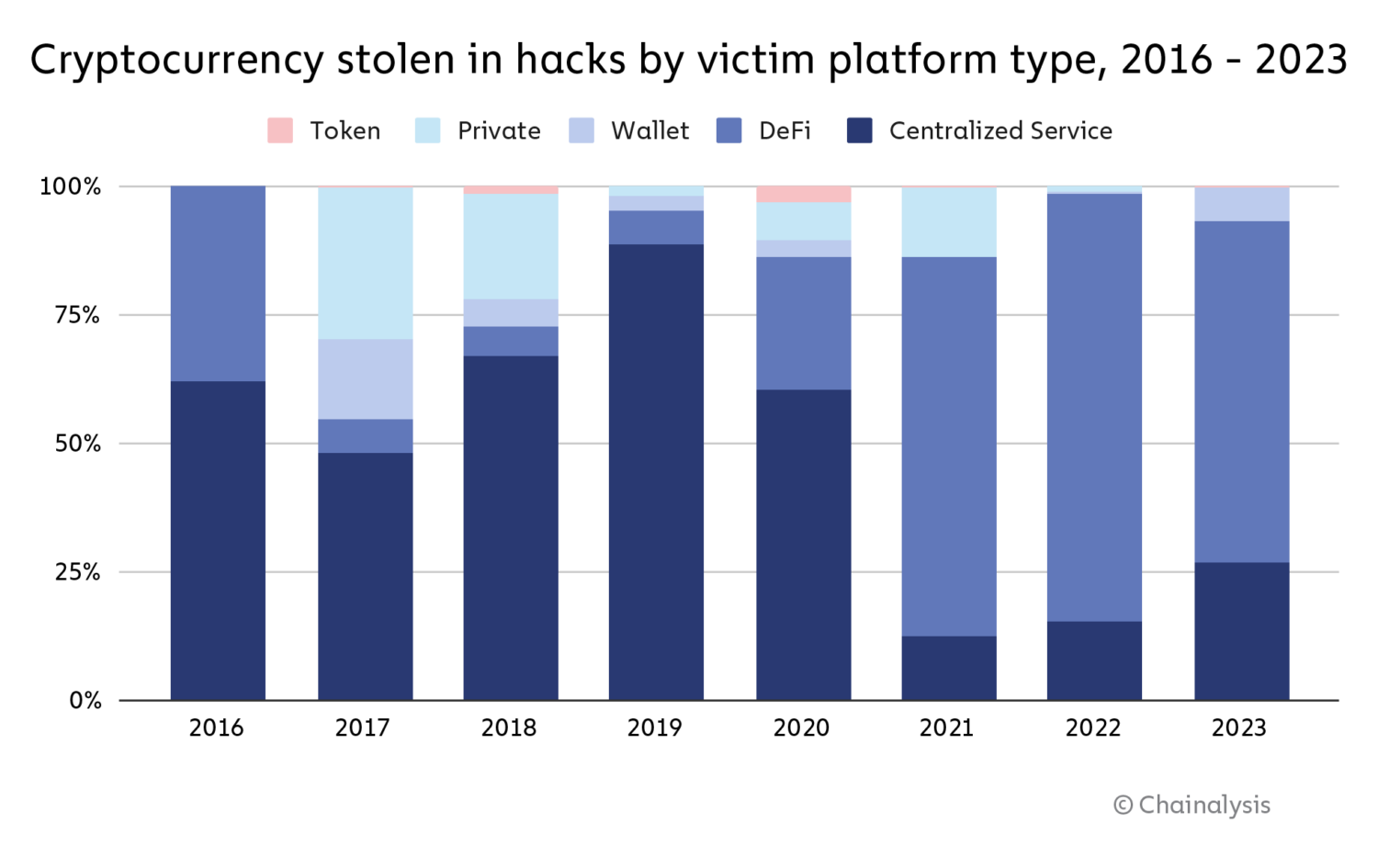
We’ll discover the potential causes for the drop in DeFi hacking in higher element in a while. Regardless of that drop, there nonetheless had been a number of massive hacks of notable DeFi protocols all through 2023. In March, for example, Euler Finance, a borrowing and lending protocol on Ethereum, skilled a flash mortgage assault, resulting in roughly $197 million in losses. July 2023 noticed 33 hacks — essentially the most of any month — which included $73.5 million stolen from Curve Finance. We will see the spikes pushed by these hacks beneath.
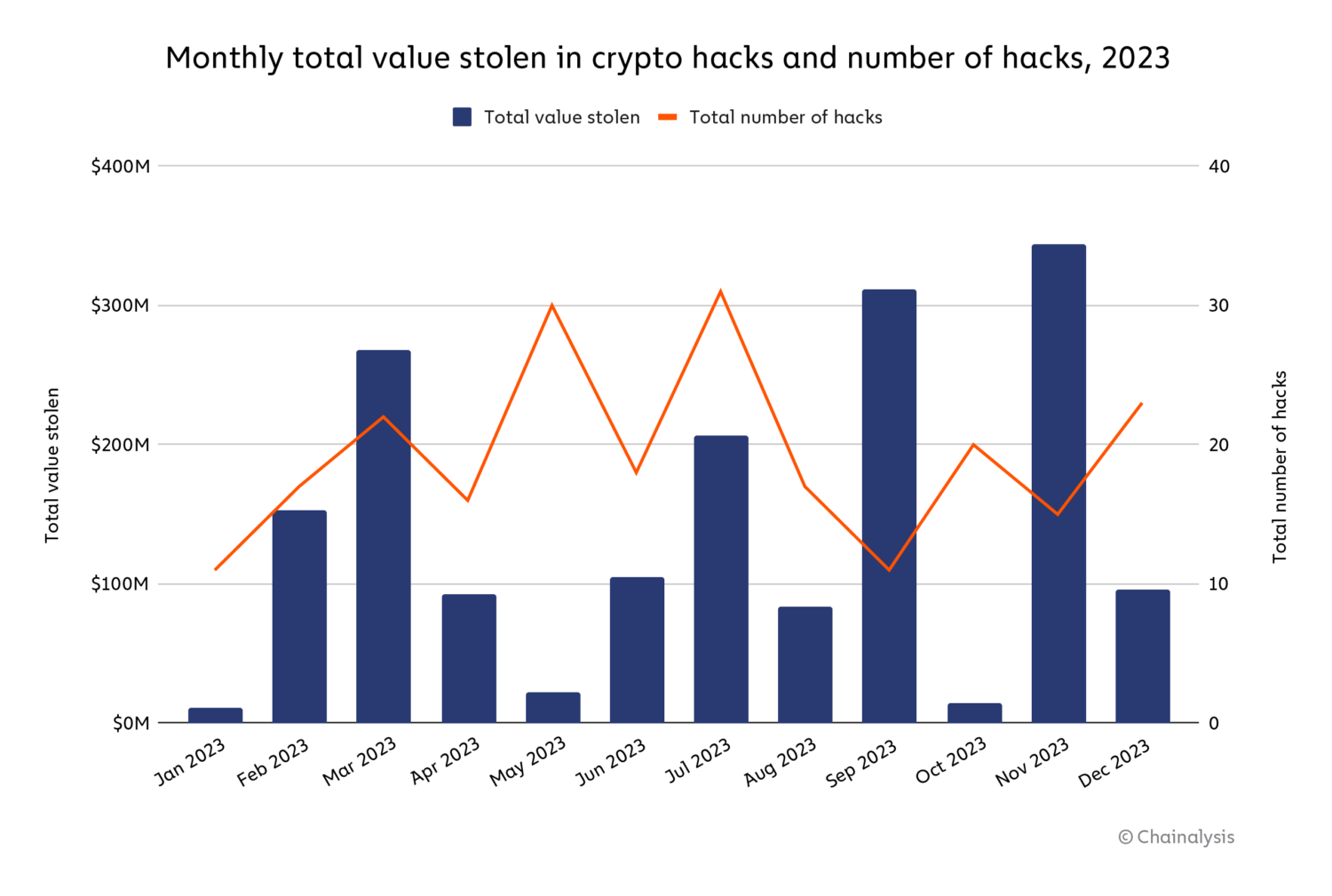
Equally, a number of massive exploits occurred in September and November 2023 on each DeFi and CeFi platforms: Mixin Community ($200 million), CoinEx ($43 million), Poloniex Trade ($130 million), HTX ($113.3 million), and Kyber Community ($54.7 million).
Maintain studying to study extra about crypto hacking tendencies in 2023, together with how North Korea-affiliated cyber criminals had one among their most lively years, executing extra particular person crypto hacks than ever earlier than.
Assault vectors affecting DeFi are subtle and numerous
DeFi hacking exploded in 2021 and 2022, with attackers stealing roughly $2.5 billion and $3.1 billion, respectively, from protocols. Mar Gimenez-Aguilar, Lead Safety Architect and Researcher at our accomplice Halborn, a safety firm specializing in web3 and blockchain options, informed us extra in regards to the rise in DeFi hacking throughout these years. “There’s been a worrying trend in the escalation of both the frequency and severity of attacks within the DeFi ecosystem,” she defined. “In our comprehensive analysis of the top 50 DeFi hacks, we observed that EVM-based chains and Solana are among the most targeted chains, largely due to their popularity and capability to execute smart contracts.” When analyzing this pattern final yr, safety specialists informed us that they consider many DeFi vulnerabilities stemmed from protocol operators focusing totally on progress, and never sufficient on implementing and sustaining sturdy safety programs.
Nevertheless, for the primary time since DeFi’s emergence as a key sector of the crypto financial system, the yearly complete stolen from DeFi protocols fell — and fell considerably.
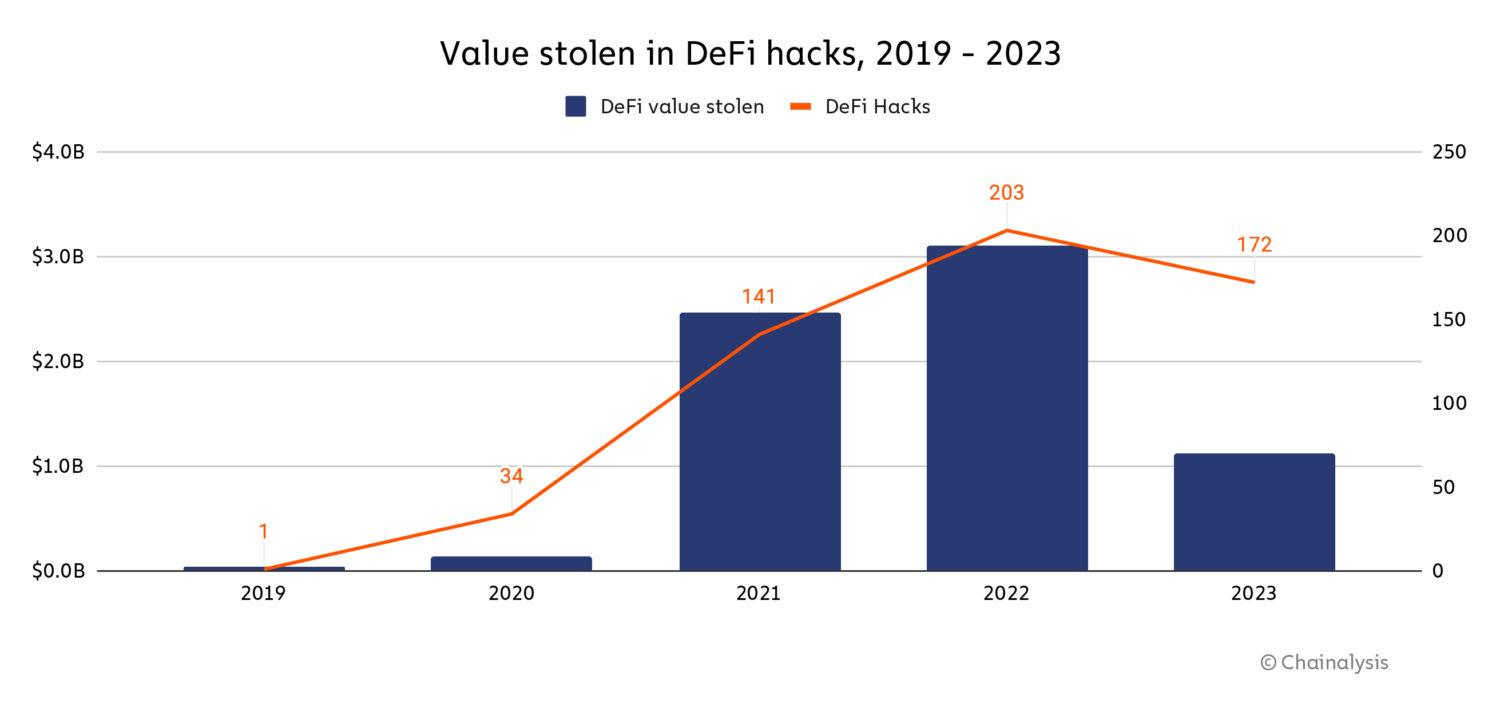
The worth misplaced in DeFi hacks declined by 63.7% year-over-year in 2023, and median loss per DeFi hack dropped by 7.4%. And, whereas the variety of particular person crypto hacks rose in 2023, the variety of DeFi hacks particularly declined by 17.2%.
So as to perceive this pattern higher, we labored with Halborn to research 2023 DeFi hacking exercise via the lens of the particular assault vectors hackers utilized.
Classifying and analyzing assault vectors inside the DeFi panorama
Assault vectors affecting DeFi are numerous and continuously evolving; it’s due to this fact essential to categorise them to know how hacks happen and the way protocols would possibly be capable to cut back their chance sooner or later. Based on Halborn, DeFi assault vectors will be positioned into one among two classes: vectors originating on-chain and vectors originating off-chain.
On-chain assault vectors stem not from vulnerabilities inherent to blockchains themselves, however fairly from vulnerabilities within the on-chain elements of a DeFi protocol, reminiscent of their good contracts. These aren’t some extent of concern for centralized providers, as centralized providers don’t operate as decentralized apps with publicly seen code the way in which DeFi protocols do. Off-chain assault vectors stem from vulnerabilities outdoors of the blockchain — one instance might be the off-chain storage of personal keys in, say, a defective cloud storage resolution — and due to this fact apply to each DeFi protocols and centralized providers.
| Hack assault vector sub-category | Definition | On-chain or off-chain |
| Protocol exploitation | When an attacker exploits vulnerabilities in a blockchain element of a protocol, reminiscent of ones pertaining to validator nodes, the protocol’s digital machine, or within the mining layer. | On-chain |
| Insider assault | When an attacker working inside a protocol, reminiscent of a rogue developer, makes use of privileged keys or different personal info to straight steal funds. | Off-chain |
| Phishing | When an attacker tips customers into signing permissions, typically achieved by supplanting a respectable protocol, permitting the attacker to spend tokens on customers’ behalf. Phishing may additionally occur when an attacker tips customers into straight sending funds to malicious good contracts. | Off-chain |
| Contagion | When an attacker exploits a protocol as a consequence of vulnerabilities created by a hack in one other protocol. Contagion additionally contains hacks which might be intently associated to hacks in different protocols. | On-chain |
| Compromised server | When an attacker compromises a server that’s owned by a protocol, thereby disrupting the protocol’s regular workflow or gaining data to additional exploit the protocol sooner or later. | Off-chain |
| Pockets hack | When an attacker exploits a protocol that gives custodial/ pockets providers and subsequently acquires details about the wallets’ operation. | Off-chain |
| Worth manipulation hack | When an attacker exploits a wise contract vulnerability or makes use of a flawed oracle that doesn’t replicate correct asset costs, facilitating the manipulation of a digital token’s price. | On-chain |
| Good contract exploitation | When an attacker exploits a vulnerability in a wise contract code, which generally grants direct entry to varied management mechanisms of a protocol and token transfers. | On-chain |
| Compromised personal key | When an attacker acquires entry to a person’s personal key, which may happen via a leak or a failure in off-chain software program, for instance. | Off-chain |
| Governance assaults | When an attacker manipulates a blockchain venture with a decentralized governance construction by gaining sufficient affect or voting rights to enact a malicious proposal. | On-chain |
| Third-party compromised | When an attacker beneficial properties entry to an off-chain third-party program {that a} protocol makes use of, which supplies info that may later be used for an exploit. | Off-chain |
| Different | Both the assault doesn’t slot in any of the earlier classes or there may be not sufficient info to correctly classify it. | On-chain/ off-chain |
Supply: Halborn
Based on Gimenez-Aguilar, each on-chain and off-chain vulnerabilities current severe considerations. “Historically, the majority of DeFi hacks have stemmed from vulnerabilities in smart contract design and implementation — a large proportion of the affected contracts we examined had either not undergone any audit or had been audited inadequately,” she stated, explaining on-chain vulnerabilities. “Another notable trend is the increase in attacks as a result of compromised private keys, which underscores the importance of improvements in security practices outside of a given blockchain.”
Certainly, the info exhibits that each the on-chain and off-chain vulnerabilities Gimenez-Aguilar describes — specifically the compromise of personal keys, price manipulation hacks, and good contract exploitation — drove hacking losses in 2023.
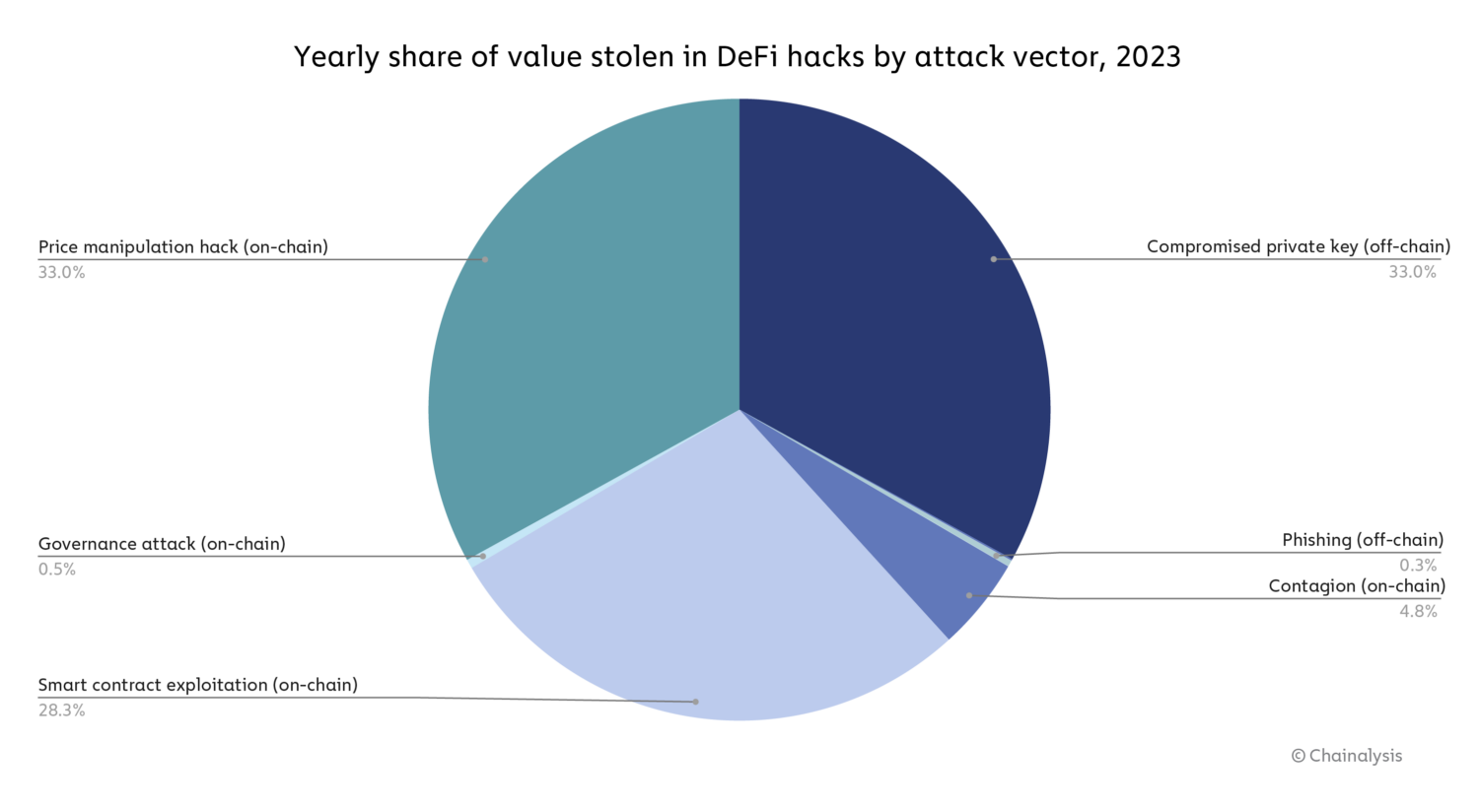
Supply: Halborn
Total, on-chain vulnerabilities drove nearly all of DeFi hacking exercise in 2023, however as we see on the chart beneath, that modified over the course of the yr, with compromised personal keys driving a bigger share of hacks within the third and fourth quarters.
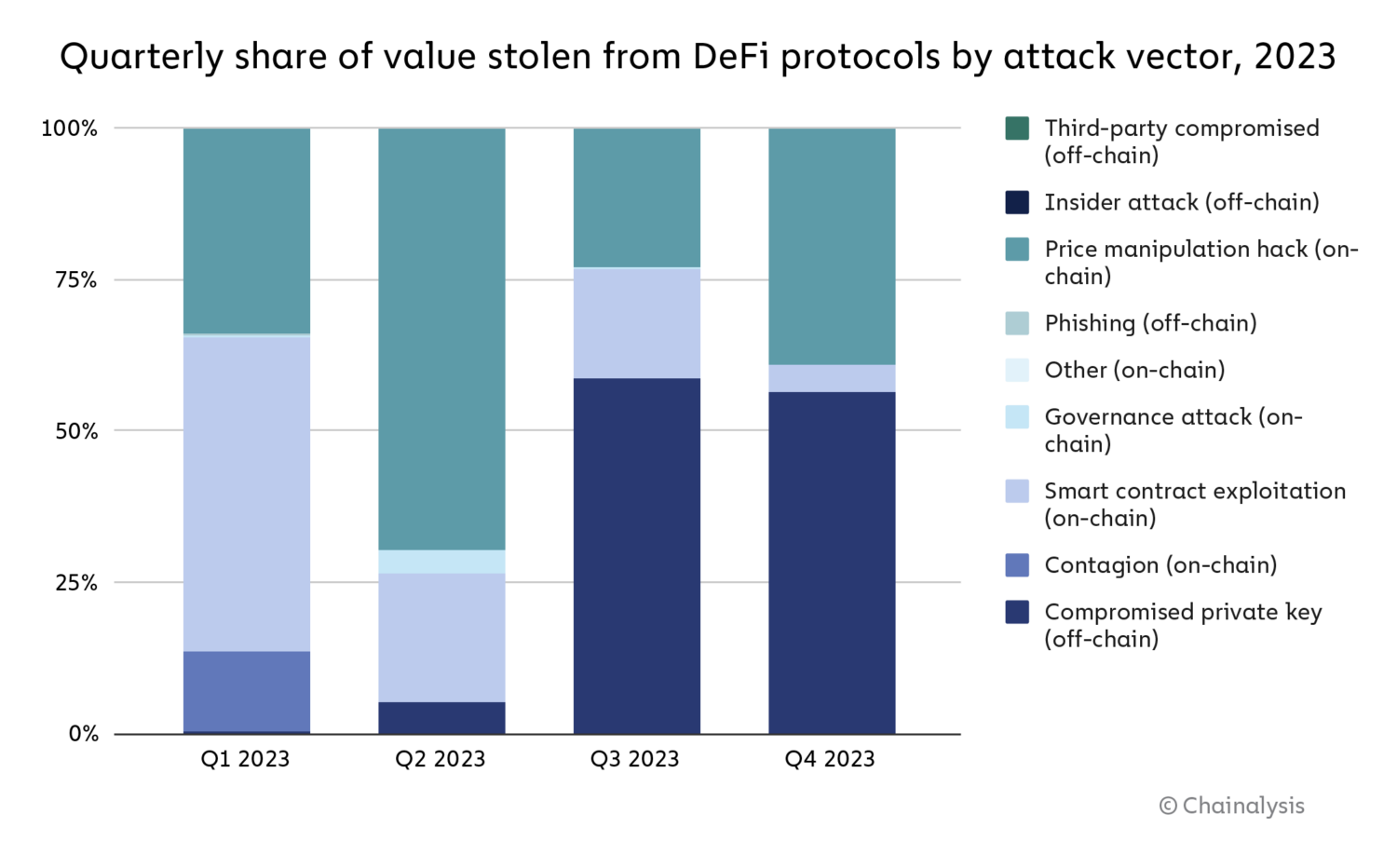
Supply: Halborn
On a hack-by-hack foundation, hacks stemming from contagion (on-chain) had been essentially the most damaging, with a median lack of $1.4 million. Governance assaults (on-chain), insider assaults (off-chain), and compromised personal keys (off-chain) observe, with all three accounting for a median hack worth of roughly $1 million.
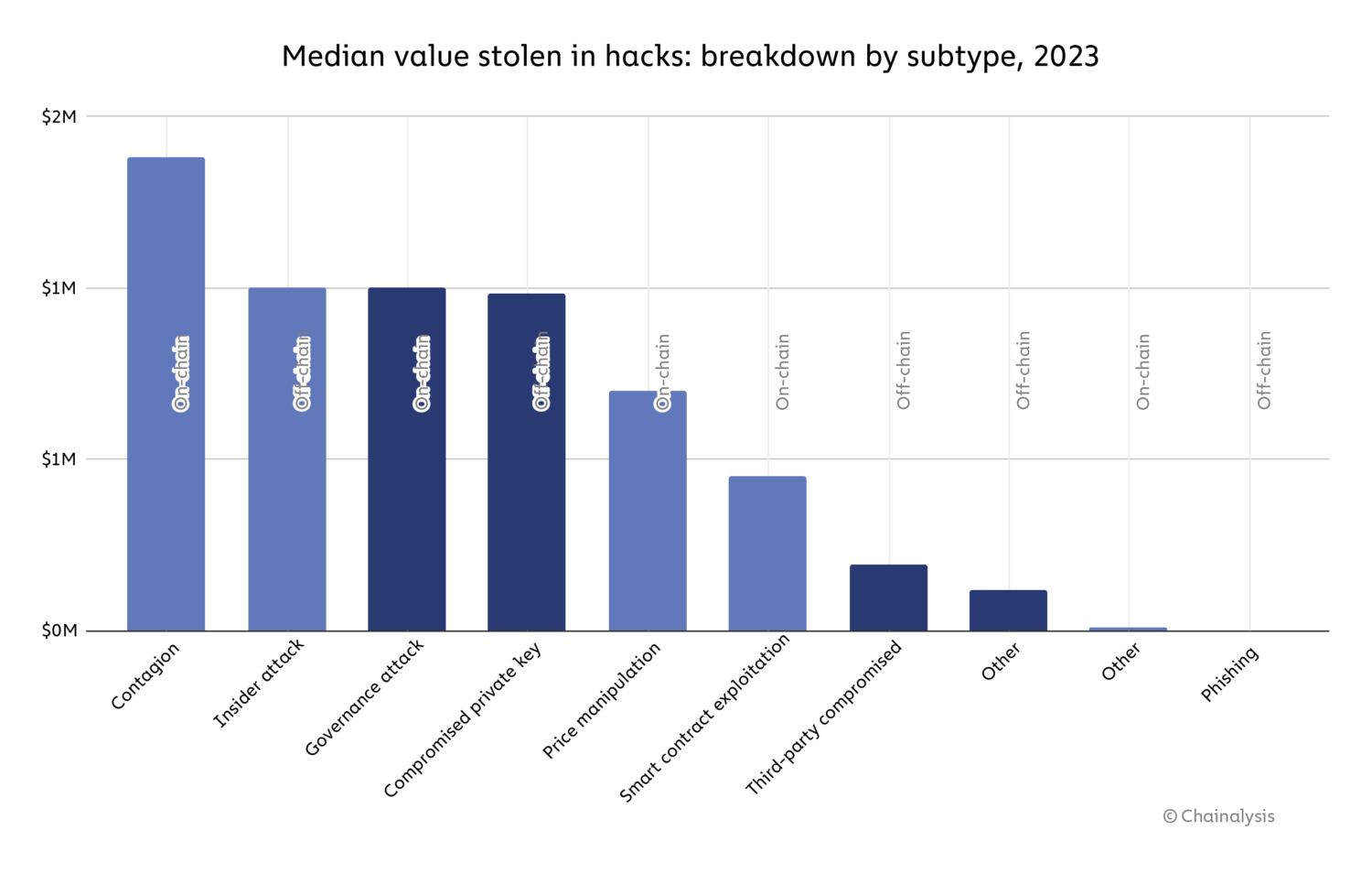
Supply: Halborn
Total although, the info supplies causes for optimism. Each the drop in uncooked worth stolen from DeFi, and the relative decline in on-chain vulnerability-driven hacking over the course of 2023 means that DeFi operators could also be getting higher at good contract safety. “I do think that the increase of security measures in DeFi protocols is a key factor in the reduction in the quantity of hacks related to smart contracts vulnerabilities. If we compare the top 50 hacks by value lost from this year with those from previous ones (studied in Halborn’s Top 50 hacks report), there is a reduction in percentage of losses from 47.0% of the total to 18.2%. Price manipulation attacks, nevertheless, remain almost constant with around 20.0% of the total value lost. This is an indication that, when performing an audit, protocols should also take into account how they interact with the whole DeFi ecosystem,” stated Gimenez-Aguilar. Nevertheless, she additionally harassed that the expansion in hacks pushed by assault vectors reminiscent of compromised personal keys signifies that DeFi operators should transfer past good contract safety and tackle off-chain vulnerabilities as properly: “Doing the same comparison as before, losses related to compromised private keys increased from 22.0% to 47.8%.” As we see above, each on-chain and off-chain vulnerabilities will be extremely damaging.
Nevertheless, Gimenez-Aguilar additionally acknowledged that the drop in DeFi hacking losses could also be pushed partly by the general drop in DeFi exercise in 2023, which can have merely decreased the variety of DeFi protocols that made ripe targets for hackers. Complete worth locked (TVL), which measures the entire worth held or staked in DeFi protocols, was down for all of 2023, following a pointy lower in the course of 2022.
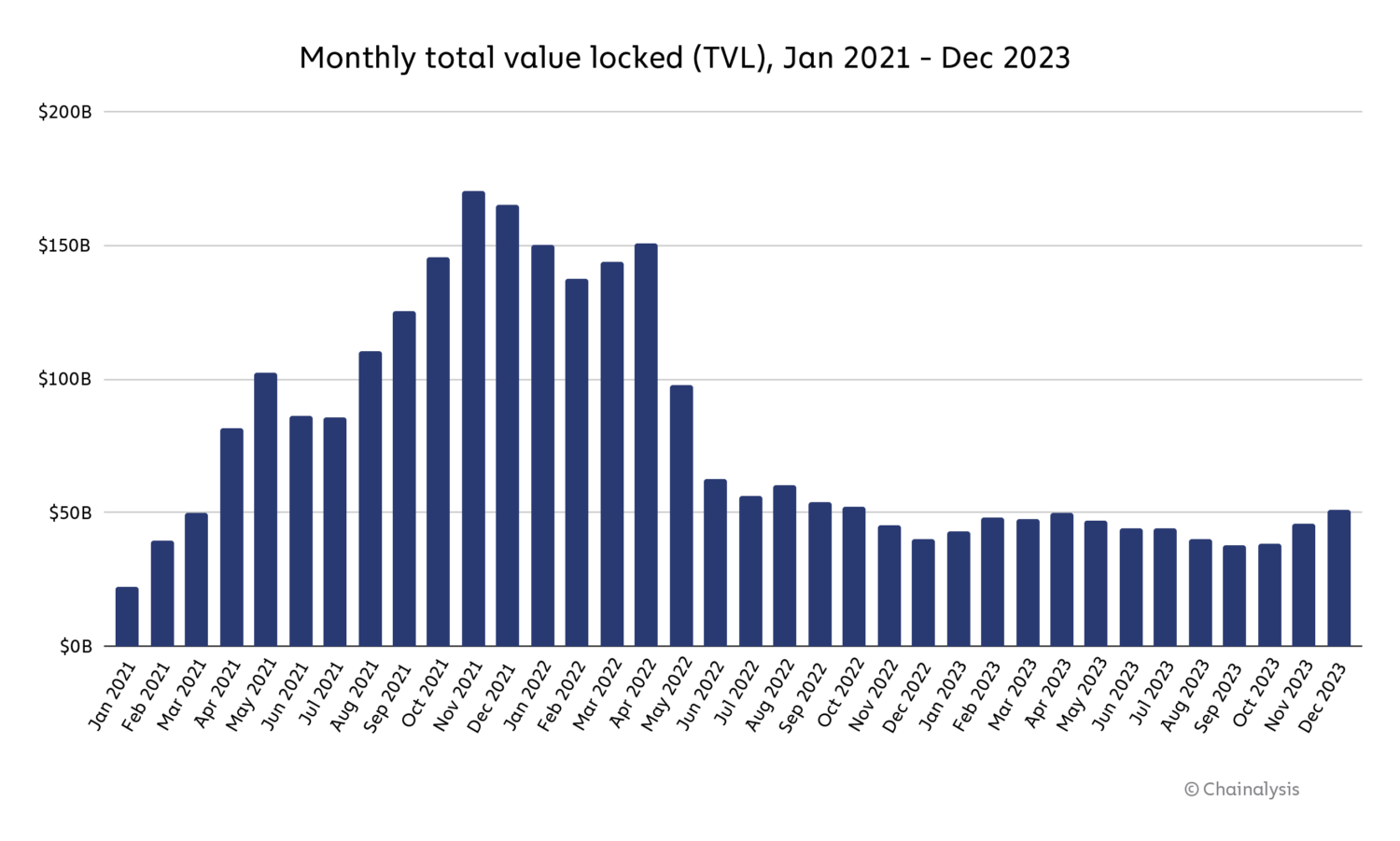
Supply: DeFiLlama
We will’t say for positive whether or not the drop in DeFi hacking was pushed primarily by higher safety practices or the drop in DeFi exercise total — most certainly, it was a mixture of the 2. However, if the lower in hacking was primarily pushed by the drop in total exercise, then it could be essential to look at whether or not DeFi hacking rises once more in tandem with one other DeFi bull market, as this is able to result in increased TVL and due to this fact a bigger pool of DeFi funds for hackers to focus on.
Regardless, there are steps DeFi operators ought to take to enhance safety. DeFi protocols weak to on-chain failures can develop programs that monitor on-chain exercise associated to financial dangers and prior platform losses. Corporations reminiscent of Hypernative and Hexagate, for instance, produce personalized alerts to stop and react to cyber assaults, which may help platforms higher safe integrations with third events reminiscent of bridges, and talk with clients who is perhaps in danger. Platforms weak to off-chain failures could goal to scale back reliance on centralized services.
North Korea hacked extra crypto platforms than ever in 2023, however stole much less in complete than in 2022
North Korea-linked hacks have been on the rise over the previous few years, with cyber-espionage teams reminiscent of Kimsuky and Lazarus Group using varied malicious techniques to accumulate massive quantities of crypto property. In 2022, cryptocurrency stolen by hackers related to North Korea reached its highest degree of roughly $1.7 billion. In 2023, we estimate that the entire quantity stolen is barely over $1.0 billion, however as we see beneath, the variety of hacks rose to twenty — the best quantity on document.
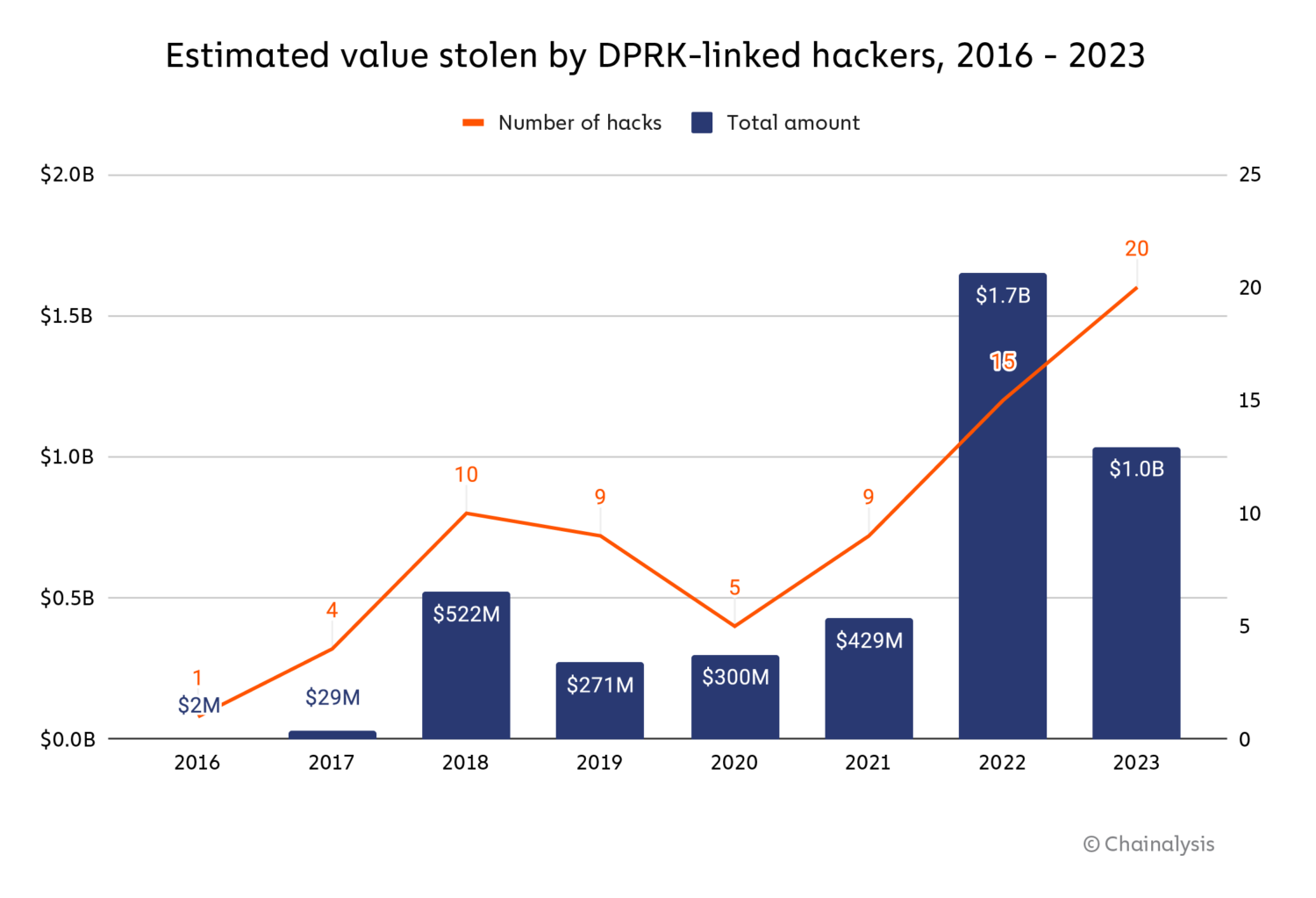
We estimate that North Korea-linked hackers stole roughly $428.8 million from DeFi platforms in 2023, and in addition focused centralized providers ($150.0 million stolen), exchanges ($330.9 million), and pockets suppliers ($127.0 million).
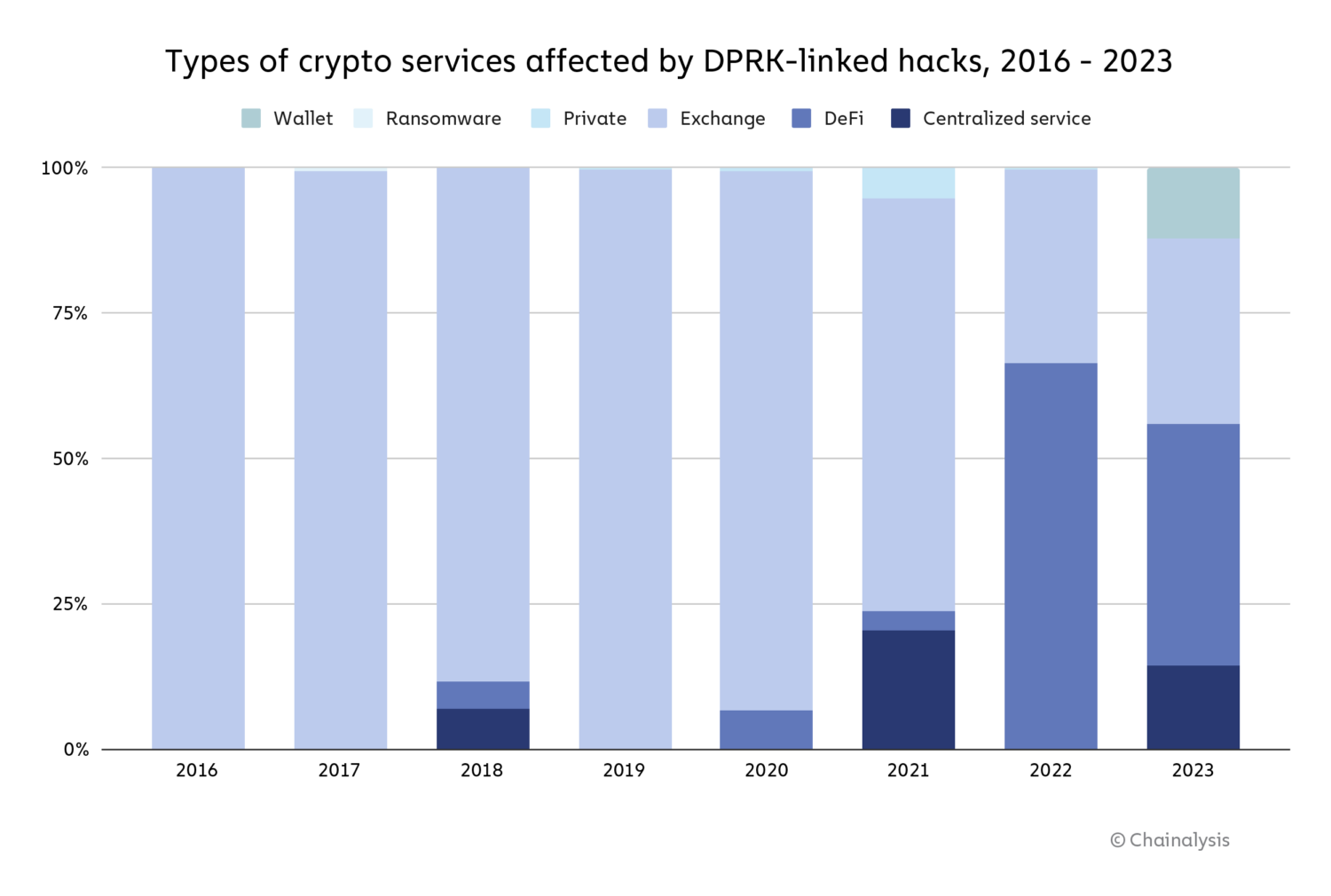
2023 noticed a notable lower in North Korean focusing on of DeFi protocols, mirroring the general drop in DeFi hacking that we mentioned above.
Case examine: The DPRK’s Atomic Pockets exploit
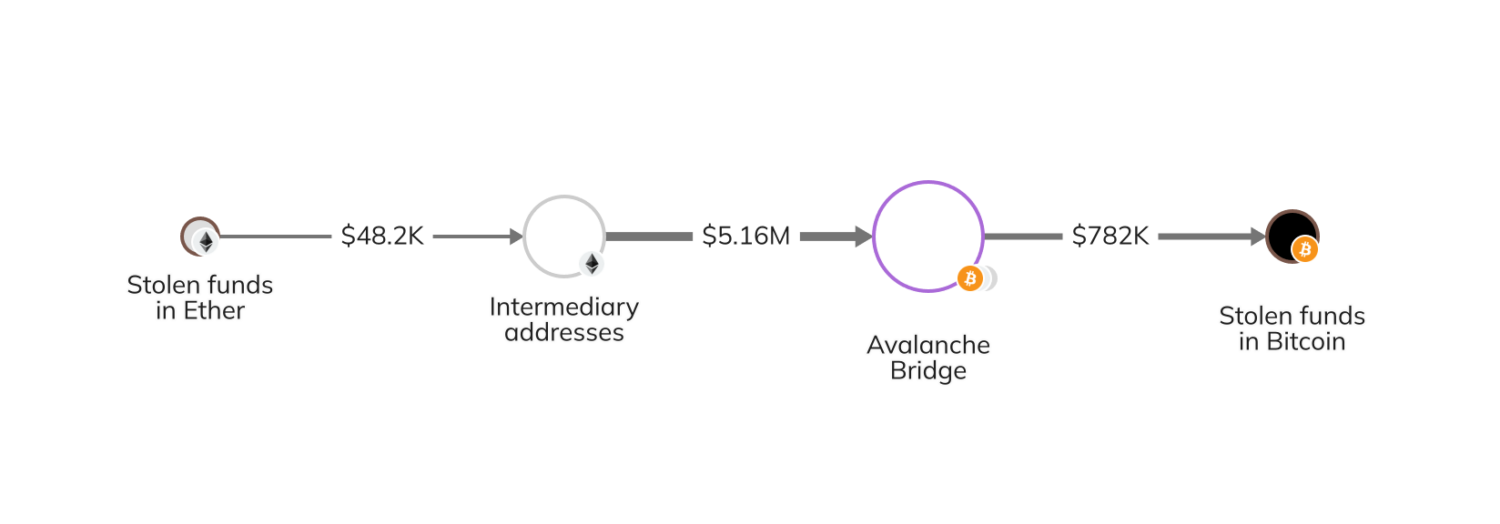
In June 2023, hundreds of customers of Atomic Pockets, a non-custodial cryptocurrency pockets service, had been focused by a hacker, resulting in estimated losses of $129 million. The FBI later attributed this assault to North Korea-affiliated hacking group TraderTraitor and acknowledged that the Atomic Pockets exploit was the primary in a collection of comparable assaults, together with the Alphapo and Coinspaid exploits later within the month. Though the specifics of how the assault occurred stay unclear, we used on-chain analysis to take a look at what occurred to the funds after the preliminary assault, which we’ve damaged down into 4 phases.
Within the first part, the attacker chain hopped — transferring property from one blockchain to a different, sometimes to obfuscate the stream of ill-gotten funds — to the Bitcoin blockchain by way of the next three strategies:
- Sending funds to centralized exchanges. Whereas we are able to’t proceed to hint funds on-chain following their motion to a centralized service, we all know on this case that funds stolen from Atomic Pockets had been transformed into Bitcoin at centralized exchanges as a result of we gathered intelligence from different trusted sources with whom we repeatedly collaborate.
- Sending funds to cross-chain bridges the place they might be moved to the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Sending funds to wrapped Ether (wETH) contracts, then transferring to the Bitcoin blockchain by way of the Avalanche Bridge.
The Chainalysis Reactor graph beneath illustrates the third methodology whereby the stolen funds (in Ether on the time) moved via a number of middleman addresses earlier than reaching the Avalanche Bridge and changing to Bitcoin.
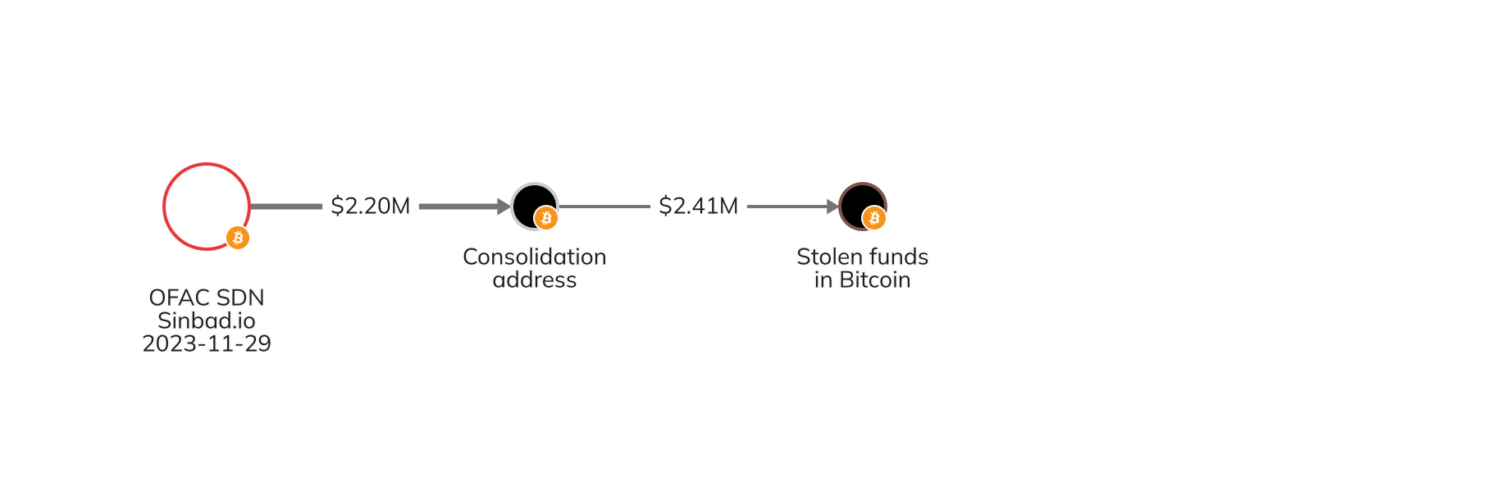
Within the second part, the attacker despatched the stolen funds to the OFAC-sanctioned Sinbad, a mixing service that obscures on-chain transaction particulars and has been beforehand utilized by North Korean cash launderers. Then, the attacker withdrew the funds from Sinbad and moved them to consolidation addresses on Bitcoin.
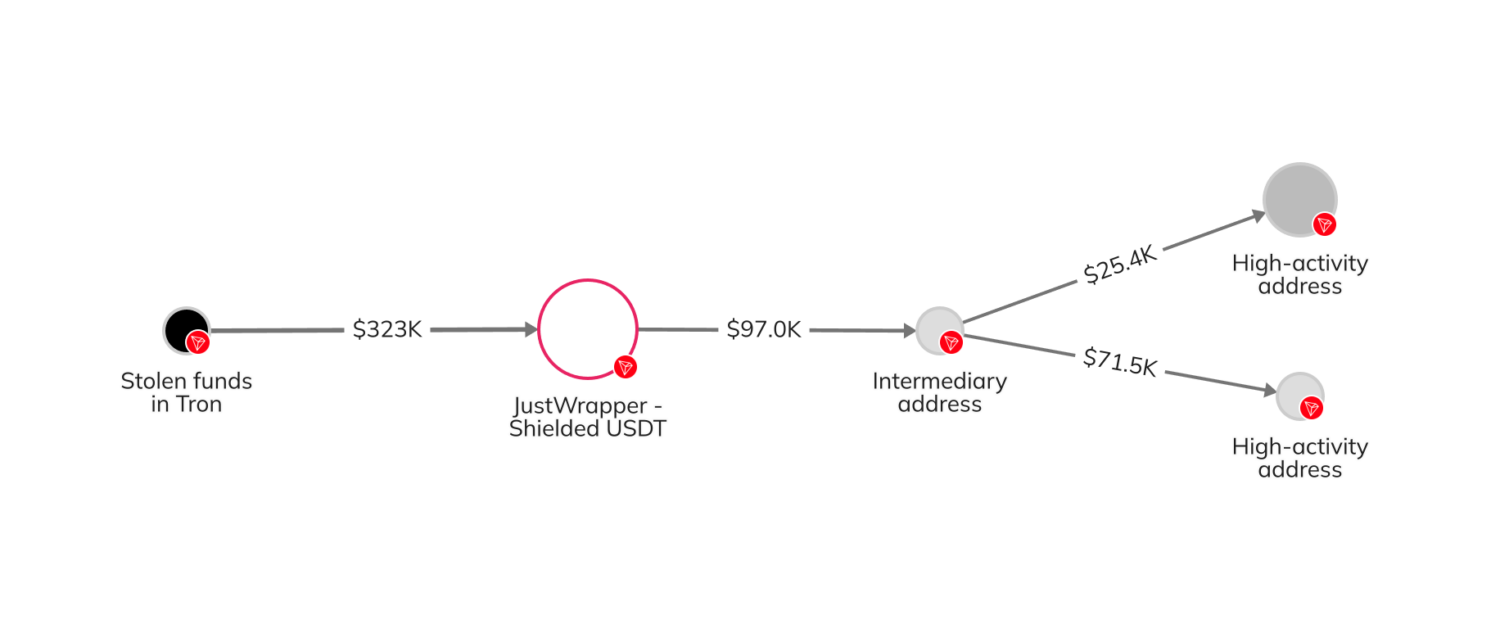
Within the third part, the attacker’s cash laundering technique shifted to focusing virtually completely on the Tron blockchain fairly than the Bitcoin blockchain. The attacker chain hopped to the Tron blockchain by way of one of many following strategies:
- Sending funds to Avalanche via the Avalanche Bridge the place they might be moved to the Tron blockchain.
- Sending funds to centralized providers, then transferring them to the Tron blockchain.
- Sending funds via further mixers or privacy-enhancing providers to additional obfuscate the stream of funds, then transferring them to the Tron blockchain.
Within the fourth and remaining part, the attacker deposited the funds at varied providers on the Tron blockchain. A few of these funds had been blended by way of Tron’s JustWrapper Shielded Pool, whereas others had been in the end despatched to high-activity Tron addresses suspected of belonging to over-the-counter merchants.
Further on-chain exercise revealed that funds stolen from Atomic had been consolidated with property from different sources earlier than transferring elsewhere, which is probably going associated to the following Alphapo and Coinspaid exploits.
The way forward for crypto hacking
Though the entire quantity stolen from crypto platforms in 2023 was down considerably from prior years, it’s clear that attackers have gotten more and more subtle and numerous of their exploits. The excellent news is, crypto platforms have gotten extra subtle of their safety and responses to assaults, too.
When crypto platforms act promptly after exploits, regulation enforcement businesses might be higher outfitted to contact exchanges the place frozen funds are situated to provoke seizure and speak to providers via which the funds flowed to collect related details about accounts and customers. Over time, as these processes enhance, it’s seemingly that funds stolen from crypto hacks will proceed to say no.
This materials is for informational functions solely, and isn’t supposed to offer authorized, tax, monetary, funding, regulatory or different skilled recommendation, neither is it to be relied upon as knowledgeable opinion. Recipients ought to seek the advice of their very own advisors earlier than making some of these selections. Chainalysis doesn’t assure or warrant the accuracy, completeness, timeliness, suitability or validity of the data herein. Chainalysis has no accountability or legal responsibility for any resolution made or some other acts or omissions in reference to Recipient’s use of this materials.
